When there are differences in parenting, remember that "avoidance is not shameful and can be useful."

Source: Family Dynamic Psychotherapist, Yuen Wai Man
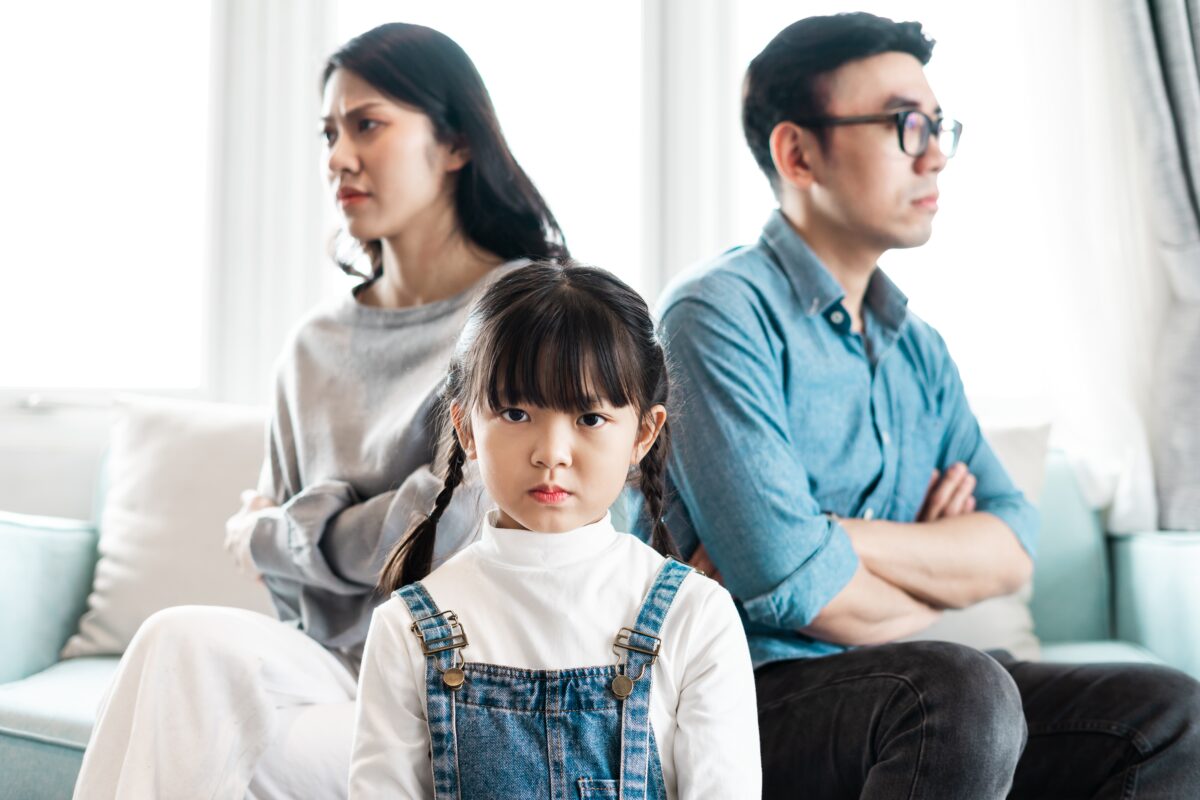
Parents’ upbringing backgrounds, education levels, or family of origin may differ in parent-child interaction, so it is quite normal for parents to have differing opinions on something.
When there are indeed different opinions, parents should find a calm environment to discuss their own perspectives and views on the problem. In any situation, we don’t want parents to argue directly in front of their children. For example, Dad can explain to Mom, “When I’m unhappy or under work pressure, I use my phone to vent and reduce stress, so I don’t think it’s a problem for kids to play with phones.”
And the wife can also express this to her husband: “Actually, I hope you can support me and understand that taking care of children is also very difficult for me.” Everyone can discuss calmly and equally in a peaceful environment. In fact, in the parenting environment, parents’ steps must be consistent.

Parents, for example, are like dancing partners in parenthood. When the father steps forward, the mother should step back. When the father raises his arms, the mother should spin around. This is a natural rhythm. If they can work together effectively, not only the dancing couple but also the onlookers can enjoy the dance. But if everyone insists on their own stance without compromise, the dance will be a mess.
In the family environment, children are often the most faithful and loyal audience, always standing in the center of the hall watching how their parents dance. So if the parents dance poorly, the audience will also be restless, the atmosphere will become tense, and more problems will arise. On the dance floor, parents will also trample on each other, causing more pain.

If there is a situation where the parents cannot see eye to eye and are in a heated argument, we would suggest that one of them leaves the scene. It’s not a matter of winning or losing or saving face, but rather allowing everyone to catch their breath and take a break. In a family environment, it’s not a competition between parents because the real victim will always be the child. So when parents are in a heated argument and cannot compromise, one of them should step back, cool down, and leave the scene. This would be better for everyone involved.